Contents
1. Domain Name System (DNS)
2. DNS Components
2.1 DNS Servers
2.2 DNS Data Base
2.3 DNS Client
3. Prerequisite Steps
3.1 Static IP Address
3.2 Steps to Assign Static IP to Server
3.3 Steps to verify your static IP
4. Domain Namespace
5. Zone Types
5.1 Primary and secondary zones
5.2 Stub zones
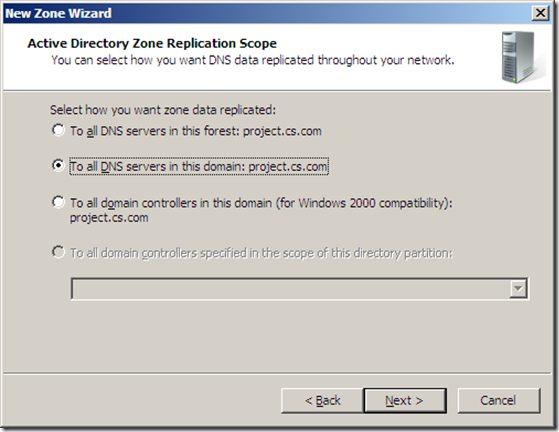
5.3 Active directory integrated zone
6. Benefits
6.1 Multi master replication
6.2 Stream line data replication
6.3 Secure dynamic updates
6.4 Backward compatible to secondary zones
7. Forward and Reverse look up
8. Dynamic updates
9. DNS Records
9.1 A [Host]:
9.2 PTR [Pointer]:
9.3 SOA [Start of Authority]:
9.4 SRV [Service Locator]:
9.5 NS [Name Server]:
9.6 MX [Mail Exchanger]:
9.7 CNAME [Alias]:
10. Zone Transfers:
10.1 AXFR [Full Transfer]:
10.2 IXFR [Incremental Transfers]:
Domain Name System (DNS)
DNS stands for Domain Name System, which is basically an internet service to translate (convert) the domain names in to IP addresses as domain names are alphabetic and easy to remember then IP addresses. A distributed database is used to implement and store this name and address information for all public hosts on the internet.
DNS Components
DNS Servers
Responsible for answering queries (Request to translate name and IP addresses).DNS server change domain names to IP addresses and locating the hosting server.
DNS Data Base
Contain information about name and IP addresses where DNS server goes to and looks for the required information (or answer to the request).
DNS Client
It sends the requests to the DNS server and communicates with DNS server for translation of host name to IP address.
Prerequisite Steps:
Static IP Address
Make sure that the server where you want to install DNS is configured with static IP. Whenever you are installing a network service on a server and you have to provide the service to clients you need static IP as you should not be a moving target.
Steps to Assign Static IP to Server
* Open start menu and Go to Network and sharing center
* On the left side of the window click on Manage Network Connections
* Right Click on the given connection and Disable it
* Now Right click and go to properties of the connection
* Click on Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IP4) and then click the properties
* Select Radio Button “Use the following IP address” and write the appropriate static IP address in the given text area
* Now right Click and Enable the Connection
Steps to verify your static IP
* Go to start menu, and open up Command Prompt as Administrator
* In the Command Prompt window Type ipconfig /all
* Notice the line “DHCP Enabled. No” which means it has static IP configuration
Domain Namespace
Domain Name space is higher archival naming convention used by DNS to locate given host name in the given domain relative to domain tree. It based on levels that are
* Root- Domain
* Top- Level Domain
* Second- Level Domain
* Sub –Domain
Zone Types
Zones come in a two different types.
Primary and secondary zones
Primary and secondary are standard zone types. This is how DNS used to work. It still can work same way but it is not common any more.
* Primary
o Master
o Read/write
o Primary is the master read write copy of the zone. Whatever server is hosting the primary zone will have the master read/write copy of the zone data base coy of the hard drive.
* Secondary
o Read only
o A DNS server hosting a secondary zone has a read only copy of the database. So no changes can be made. It has the full database it can respond to client requests and it is used for the exact purpose but updates cannot be made.
* Stub
o Only contains information about other DNS servers.
o A stub zone only contains information about other DNS servers. It does not have a full database.
* Active Directory Integrated
o DNS database is stored as an active directory object.
o Active directory integrated zones take the place of all primary and secondary. Now the DNS database is stored as an active directory object eliminating that master read/write copy having a single master. Now we can use the multi master topology that active directory provide for us.
Stub zones
* DNS allows for delegations.
* A delegation is where another DNS server has been delegated the authority over a sub-domain.
* Before stub zones, all delegations had to be managed manually.
* A stub zone allows for the automatic propagation of delegation to DNS servers.
Active directory integrated zone
Active directory integrated zone has many benefits.
Benefits
* Multi master replication
* Stream line data replication
o Now we have DNS and active directory databases together and replicate them altogether as one.
* Secure dynamic updates
o Dynamic updates can now be secure to have only clients that have been authorized by the active directory database can update the DNS server, which stop somebody generically out of the internet for updating your DNS server.
* Backward compatible to secondary zones
o In active directory integrated zone will act as a primary zone. If you have older DNS server or UNIX bind DNS server which you want to keep functioning but it does not have the mechanism to support active directory integration. Simply make old DNS server in to a secondary zone DNS server pointing to one of the active directory integrated DNS servers as its primary and everything will work just fine.
Forward and Reverse look up
* Forward look up
o Name to IP address
o Widely used
* Reverse Look up
o IP address to name
o Not always needed
o Usually used to meet the needs of a particular application (very often for validation purposes)
]Dynamic updates
* Before dynamic updates all DNS information was manually entered.
* Now records can be dynamically added (or updated) from the client.
* Updates can be secured with active directory integrated zones. (Authorized users)
* Dynamic updates can be integrated with other network services. (I.e. DHCP).
o DHCP inform DNS to make a record that an IP address has been given.
DNS Records
The record can be added to the zone files we create. With the help of standard DNS query the DNS Resolver class resolves the domain names.As a result of the DNS query there is a DNS response that contains the DNS record for that query. And this DNS record contains the information depending upon the type of DNS resource record. There are many DNS record of different types but some of the records are commonly used. These are following:
A [Host]:
The A record or Host record resolves the Host name in to IP addresses and it is a typical Forward Lookup Record. And A Record maps an IPv4 address to a hostname.
PTR [Pointer]:
The PTR or Pointer Record resolves the IP addresses to a Host name and it is exactly opposite to the A or Host Record and also called a Reverse Lookup Record
SOA [Start of Authority]:
This is the first record in any zone file and it is most authoritative for the zone.It gives the foundation and the starting point for the zone database. The SOA Record is added automatically created when we add a zone.
SRV [Service Locator]:
SRV Service Locator Records are used to represent a certain service that a computer is may be offering. They are typically use in conjunction with active directory.Active Directory requires DNS in order for its clients to locate the presence of domain controllers. When a user attempts to login for instance the client machine go out to its DNS Server to find the domain controller for the particular domain. It is the SRV Resource Record that resolves the query and directs it towards the domain controller services for that particular domain. The A record works in correspondence with the SRV Record to resolve the hostname in to IP addresses.
NS [Name Server]:
The Name Server or NS Record identifies the DNS Servers that are authoritative in each zone. And it specifies a name server for the particular domain that allows the DNS lookups within the different zones in the domain.
MX [Mail Exchanger]:
The MX or Mail Exchanger Record is used to help email give from one point to another suppose when you want to send an email to some body at sbk.edu.pk there are the DNS server over the internet that have MX or Mail Exchanger Record which point to our Email server. The Mail Exchanger Record specifies a mail exchange server for the particular domain that allows the mails to deliver to that particular mail server in the domain.
CNAME [Alias]:
The CNameor Canonical Name or simply refers to Alias some times. The CNAME Record resolves the Alias to a host name. For example when you go to www.microsoft .com then now the Microsoft might have the web server named webserv1.microsoft.com.when any body types www.microsoft .com the CNAME Record has been actually created where www.microsoft.com is directed to webserver1.microsoft.com.
Zone Transfers:
Zone transfers are only used with the Standard zones that are Primary and Secondary Zones. They cannot use with Active Directory Integrated zone. Replication takes place in active directory integrated zone as part of active directory replication. When we use standard zones Primary or Secondary we use Zone Transfers for this replication. There are two different types of zone transfers
AXFR [Full Transfer]:
AXFR means transfer the entire database. Older version of DNS has to do it every time there is an update. AXFR is really only used when we first create a secondary zone to get the entire database to come over or for the recovery of database.
IXFR [Incremental Transfers]:
IXFR is used to for the incremental transfers and most commonly used now days. IXFR is used to save our bandwidth so that when changes made only that changes must be added to the secondary.
Note: The DNS Zone Transfers can be a Security risk as there are number of issues surrounding zone transfers for example a hacker might be able to create the DNS Server and can tell your primary database that it is the secondary database through all the data here. Zone transfers are less secured then the Active Directory Integration.

![SERVER 2008 ADDS (80)[1] SERVER 2008 ADDS (80)[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiGyoi040FbjJ2IXDHsTkogSsGqrpfF_jZhOVMsPBlh44XhKcW3GR0Cm4B4c6NaIVKPSLTczSHkPo46H7jaffctK6J6uvjytUYQYeJ3fc-BkTsmipJMwmJ-kPWNqs3r8sANRvgHeBiCeZ4/?imgmax=800)
![SERVER 2008 ADDS[1] SERVER 2008 ADDS[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEira0T61hOtsPoE6a64CKo0K3DEaaWJKIHDBJsmCOtKcS7zmD1dZ4VEgCsaOKz8AttGmfUH4FmMvldyuiF2DsjUpb_KtcppSsXGN6EtcAbBcyjigwYKJwPyV8AaqzV8d4Dy7-uMXSlFoqg/?imgmax=800)
![SERVER 2008 ADDS (1)[1] SERVER 2008 ADDS (1)[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj1KfX6yzepGFeMO-eLVzKkNmfCBa-OAykqxn5su1NRTVjoRyokelfqog82jI-qORSO21WMxBOieGyFwvsgh-ReSqgiCxc2FOp5qfy4T9hic6Ho4VwAu3M7JsqBl1Z-9JAns6QGyCKJfO0/?imgmax=800)












 Previous Article
Previous Article





